Import
Operations can be created using manual data entry. However, it is much easier to import metadata automatically from other systems. Almost any system can be connected via an appropriate plugin if it supplies machine-readable data. Two different types of plugins are generally available for this purpose:
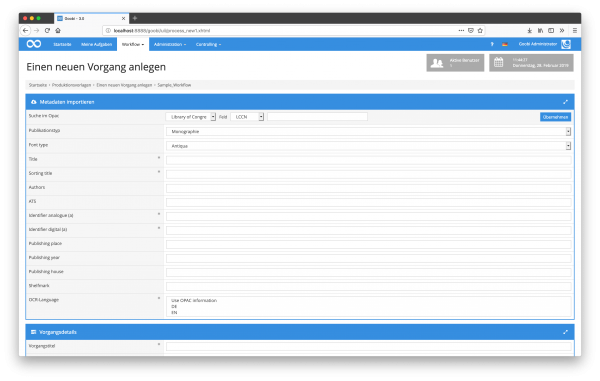
Catalog plugins
Be it the central library catalogue, the index in the archive or the object database in the museum. Using standardized interfaces such as z39.50, SRU or OAI, metadata can be retrieved and processed in any format, including MARCXML, Lido or DublinCore. But proprietary interfaces with their own formats can also be used (e.g. XML via a REST interface).
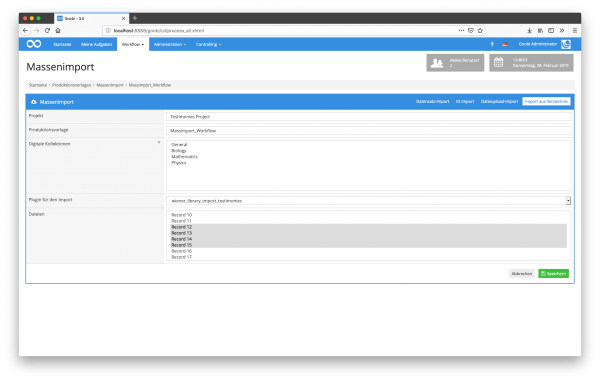
Import/ Mass Import Plugins
Often metadata and digital objects are available as results of earlier projects and in larger quantities. Or Excel tables, CSV files together with special folder structures, Microsoft Access databases or other proprietary developments are available in proprietary formats. Even such data is no big problem for Goobi workflow. Even in such cases, the data can be transferred and imported using individual import plug-ins.
Processing
The strength of Goobi workflow lies in the processing and control of workflows. For this purpose, the desired workflows are stored in advance in repeatedly applicable production templates. Such a production template describes any number of tasks, which in turn are subject to a predefined sequence. Typical examples of production templates include these:
- Standard workflow for digitization and publishing
- Digitization on Demand
- Mass import of a legacy data project
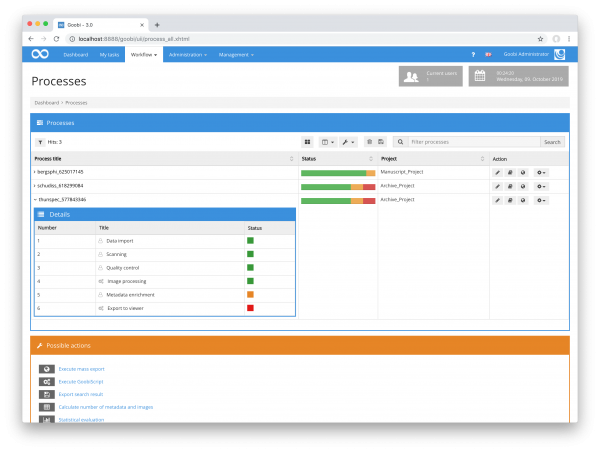
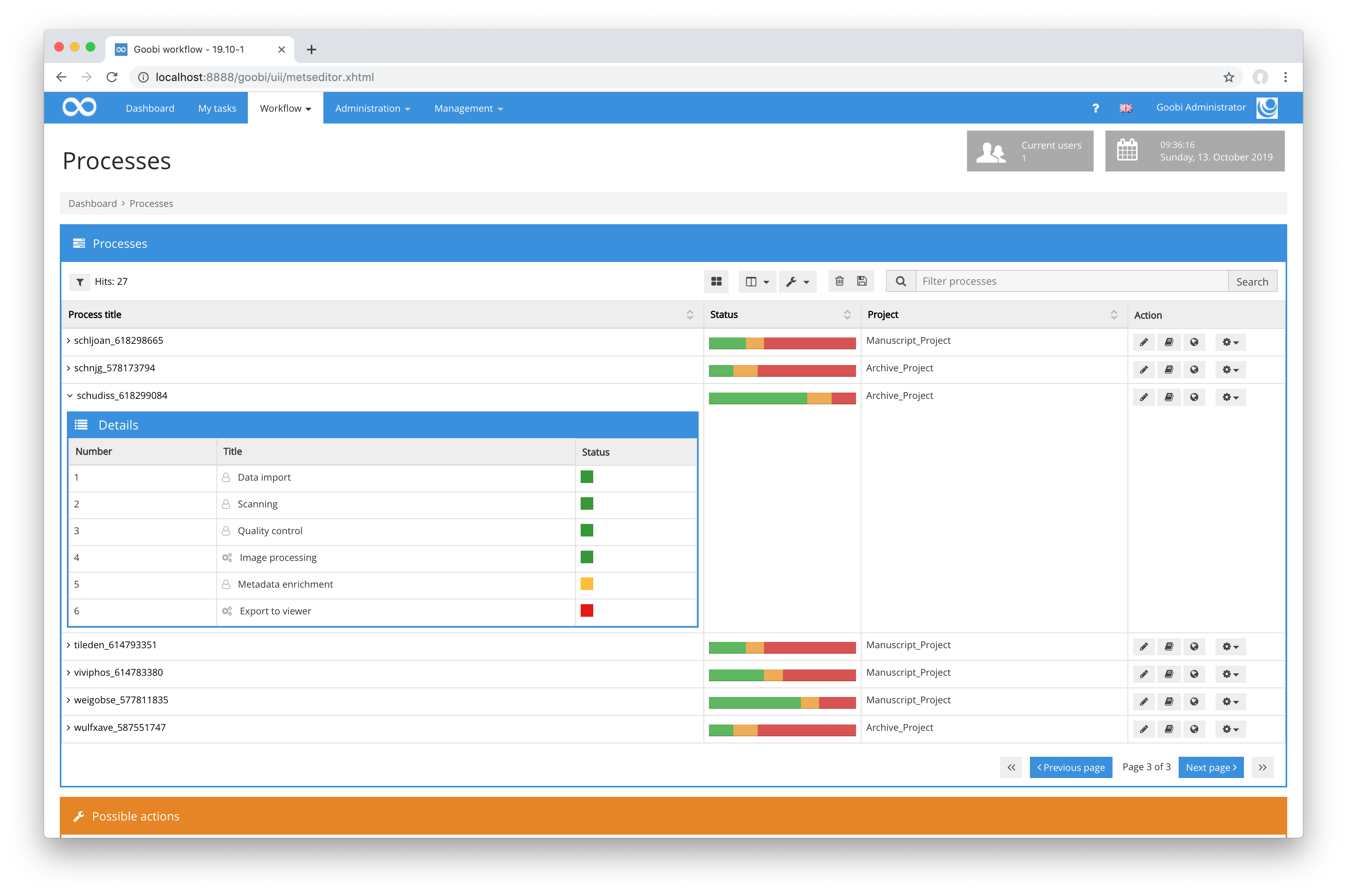
On the basis of such a production template, a process is created in Goobi for each object to be digitised. This then allows the tasks taken over from the production template to be processed. Each of these tasks is assigned to at least one user group or user and receives various rights, functions or plug-ins for data processing and validation. In this way, among other things, it is controlled whether such a task is executed manually by a user or fully automatically by the server.
For example, a prototypical workflow for digitizing books can consist of the following tasks:
| Task | Type | Responsibility | Description |
| Creation of the process via catalogue query | Manually | Librarians | check the data record in the catalog, create a process by automatic data transfer from the catalog |
| Scanning | Manually | Scan-Operator | Creation of the digital copies and import into Goobi workflow |
| Validation of images | Automatic | Server | Automatic validation of correct color depth, resolution and file naming |
| Quality Control | Manual | Quality Assurance | Sample-based examination of the scan quality with regard to completeness and sharpness |
| Producing Derivatives | Automatic | Server | Automatic creation of a compressed derivative next to the master images |
| Structure and Metadata Capture | Manual | Librarians | Generation of a pagination, generation of structural data, enrichment of metadata |
| OCR Generation | Automatic | Server | Automatic full-text recognition and save as ALTO files |
| Generation of persistent identifier | Automatic | Server | Automatic generation of persistent identifiers and registration of identifiers with a resolver |
| Exports the data to the Goobi viewer | Automatic | Server | Automatic publication of the digitized material including metadata in the Goobi viewer with configured access restrictions |
| Enrich master images with XMP metadata | Automatic | Server | Automatic enhancement of master images with XMP metadata from the Goobi process metadata |
| Ingest the master images into a repository | Automatic | Server | Automatic ingest of master images into a repository (e.g. Fedora) |
Within Goobi workflow, the workflows and associated tasks are visualized as follows:
In addition to the core functions of Goobi workflow, a large number of different plug-ins are available as extensions. There are currently about 210 such plug-ins of different types. Project managers can, for example, use the statistics and administration plug-ins to monitor and evaluate the exact progress of the project and generate reports. The administrators of Goobi workflow, on the other hand, have powerful tools at their side with which mass manipulations can be carried out on the database in a simple manner.
Export
At the end of a workflow there is generally the export. This is also plugin-supported. Typical export plug-ins realize the transfer of images and metadata in standardized formats such as METS/MODS or LIDO format to a presentation system such as the Goobi viewer. But export plug-ins are also available for other application scenarios, such as for generating PDF files and sending e-mails with download links, or for ingesting data into a repository or long-term archive.